Many people enjoy spending time outdoors, but not everyone understands the risks of sun exposure.
Sunburn is a common issue that can arise when skin is overexposed to ultraviolet (UV) light.
The skin reacts to this excessive UV radiation through an inflammatory response, resulting in the painful redness and sensitivity characteristic of sunburn.
Different skin types respond to UV exposure in various ways.
Those with lighter skin are more susceptible to sunburn because they have less melanin, a pigment that offers some protection against UV rays. This means that individuals with fair skin often need to take greater precautions when enjoying outdoor activities under the sun.
Understanding Sunburn and UV Radiation
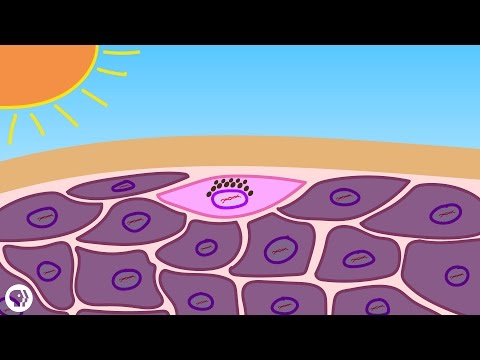
Sunburn occurs when skin is overexposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This section explains the science behind sunburn, different types of UV light, and how these rays affect skin cells at a cellular level.
The Science of Sunburn
Sunburn is an inflammatory response resulting from excessive UV exposure. The skin contains cells called keratinocytes, which make up the outer layer.
When UV radiation penetrates the skin, it can damage the DNA within these cells. This damage triggers the body to react with inflammation.
Symptoms of sunburn include redness, pain, and swelling. In severe cases, blisters may form as the skin attempts to heal itself. The body’s response aims to protect against further damage, but repeated sunburn can lead to long-term effects, including an increased risk of skin cancer.
Types of Ultraviolet Light
There are two primary types of UV radiation that contribute to sunburn: UVA and UVB.
-
UVA rays penetrate deeply into the skin and are linked to skin aging and the formation of wrinkles. They can also contribute to DNA damage over time.
-
UVB rays, on the other hand, are responsible for the more immediate effects of sunburn. These rays damage the superficial layers of the skin and cause the characteristic redness and pain.
Both types of UV radiation can lead to skin mutations. Protection against both UVA and UVB is essential to minimize skin damage and reduce cancer risks.
Effects of UV Radiation on Skin Cells
When skin cells are exposed to UV radiation, changes occur at the molecular level.
The DNA in skin cells can suffer from mutations due to the energy from UV light. This damage might initiate a process called apoptosis, where damaged cells self-destruct. This mechanism helps prevent the transformation of cells into cancerous ones.
Moreover, prolonged exposure to UV light can compromise the skin’s ability to repair itself. The sustained RNA damage impairs the production of proteins essential for cellular health. Understanding this cellular response highlights the importance of sun protection measures, such as using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing.
Preventing Sunburn and Protecting Skin Health
Taking steps to prevent sunburn is essential for maintaining skin health. Various strategies can be employed, ranging from the selection of appropriate sunscreens to the use of protective clothing. Understanding these approaches helps reduce the risk of sun damage and its long-term effects.
Sun Protection Strategies
Effective sun protection strategies begin with awareness of sun exposure times. It is best to avoid direct sunlight between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV rays are strongest.
Seeking shade when outdoors can greatly reduce exposure. Regular application of sunscreen is critical, even on cloudy days.
Additionally, wearing hats and sunglasses can protect the face and eyes. When selecting outdoor activities, consider those that provide natural shade, like picnics under trees. Staying hydrated and monitoring skin for any changes can further enhance protection.
Choosing the Right Sunscreen
Selecting the right sunscreen is vital for effective skin protection.
A broad-spectrum sunscreen is recommended, as it blocks both UVA and UVB rays. Look for sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher for optimal protection.
Ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are beneficial due to their physical blocking properties.
Sunscreen should be applied generously and re-applied every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating. Checking the expiration date is also important, as expired products may not provide adequate protection.
Clothing and Accessories for Sun Safety
Clothing plays a significant role in sun safety.
Wearing long sleeves, pants, and a wide-brimmed hat can shield the skin from harmful rays. Look for fabrics with a high Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) rating, which offers better protection than regular clothing.
Darker colors generally absorb more UV radiation, providing additional shielding.
Accessories like sunglasses are essential, as they protect the eyes from UV rays. They should block 100% of UVA and UVB rays. Cotton and linen are good choices for daily wear, as they are breathable while still offering coverage.
By combining these methods, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of sunburn and promote healthier skin.
Consequences of Excessive Sun Exposure
Excessive sun exposure can lead to serious health risks and visible skin changes. This section explores immediate and long-term effects on the skin, the potential for developing skin cancer, and the signs of premature aging. Understanding these consequences is crucial for sun safety.
Immediate and Long-Term Skin Damage
Sunburn is one immediate reaction to too much ultraviolet (UV) light. Symptoms include erythema, or redness, and may also feature blisters in severe cases. Sunburn occurs when the skin’s collagen and elastin fibers are damaged, leading to inflammation.
Long-term exposure to UV rays results in cumulative skin damage. This can manifest as photoaging, speeding up the aging process. Research shows this damages skin integrity, increases wrinkles, and diminishes skin elasticity. Over time, the skin becomes thinner and less resilient, making it more susceptible to injury.
Skin Cancer: Risks and Types
Excessive sun exposure raises the risk of skin cancer types, primarily basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Each type has varying severity and treatment approaches.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common, usually appearing as a slightly raised, pearly bump. Squamous cell carcinoma may look like a red, scaly patch. Melanoma, while less common, is more aggressive and can spread quickly if not detected early.
The risk for these cancers increases with sunburn history and prolonged exposure. Young adults and children are particularly vulnerable, making early protective measures vital.
Visible Signs of Skin Aging
Signs of premature aging often appear due to excessive UV exposure. This includes early development of wrinkles and liver spots.
The sun breaks down collagen, a vital protein that provides structure and firmness to the skin. Additionally, photoaging can result in uneven skin tone or texture.
Fine lines may appear around the eyes and mouth, and skin may lose its youthful glow. Protecting skin from UV rays can significantly delay these visible signs and maintain overall skin health.
