In photography, understanding the concepts of focal point and focal length is vital for creating stunning images.
The focal point is the specific area of an image that is in sharp focus, while the focal length refers to the distance measured in millimeters between the lens’s optical center and the camera’s sensor. This distinction plays a crucial role in how photographers compose their shots and achieve the desired effect in their work.
Focal length is an essential characteristic of a lens and directly impacts the angle of view and magnification of the subject.
A longer focal length can bring distant subjects closer, while a shorter focal length captures a wider scene. Knowing how to manipulate these elements helps photographers enhance their craft and convey the right message through their images. Resources such as detailed articles can provide further insights into these principles.
By grasping the difference between these terms, photographers can make informed decisions about their equipment and shooting techniques. This understanding not only improves technical skills but also fosters creativity in photography.
Understanding Focal Length and Its Impact on Photography

Focal length plays a crucial role in photography by influencing how images are captured. It affects the angle of view and magnification, which are key for different photography styles.
Additionally, understanding focal length helps in selecting the right lens for various photographic needs.
Defining Focal Length and Focal Point
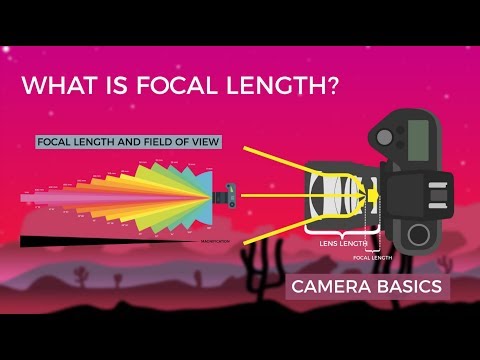
Focal length is the distance between the lens’s optical center and the camera sensor, measured in millimeters. It determines how much of a scene will be captured in an image.
A wide-angle lens, with a short focal length, creates a broad view, ideal for landscape photography. In contrast, a telephoto lens has a long focal length, allowing for close-up shots from a distance, which is beneficial in wildlife photography.
The focal point refers to where the light converges to create a sharp image. Understanding both concepts is critical for photographers aiming to control perspective and depth of field in their work. Different lenses, such as prime and zoom lenses, will have varying focal lengths that cater to specific photographic styles.
The Role of Focal Length in Field of View and Magnification
Focal length directly affects the field of view and magnification. A shorter focal length, such as that found in a wide-angle lens, provides a wider angle of view, making it perfect for tight spaces or large subjects.
For example, when capturing architectural photography, a wide-angle perspective can include more of a building in the frame.
Conversely, longer focal lengths, typical in telephoto lenses, compress the scene and magnify distant subjects. This is particularly useful for sports photography or portrait photography where the subject should stand out against a blurred background. Photographers must also consider the crop factor, which can affect field of view based on the camera sensor size.
Choosing the Right Lens for Different Types of Photography
Selecting the appropriate lens based on focal length enhances the photography experience. For landscape photography, wide-angle lenses are preferred to capture expansive views, offering a sweeping perspective.
In portrait photography, lenses around 50mm to 85mm are often chosen for their flattering perspective.
Wildlife photography typically utilizes telephoto lenses, which allow photographers to capture animals without disturbing them.
Other styles, like real estate photography, may benefit from ultra-wide-angle lenses to make spaces appear larger and more inviting. Each lens type serves a distinct purpose and can significantly impact the quality and composition of the images produced.
Exploring the Relationship Between Focal Length and Optical Quality
Focal length plays a vital role in determining optical quality in photography. Key aspects include how it affects depth of field and the presence of visual distortions. Understanding these relationships is crucial for photographers aiming to achieve specific artistic effects.
Focal Length’s Influence on Depth of Field and Bokeh
Focal length significantly impacts depth of field, which refers to the zone of acceptable sharpness in an image.
Short focal lengths, typically found in wide-angle lenses, create a deeper depth of field. This means more of the image appears in focus, making them ideal for landscapes or group scenes.
In contrast, long focal lengths, commonly in telephoto lenses, give a shallow depth of field. This effect is favored in portrait photography, where the subject stands out against a blurred background, enhancing the aesthetic known as bokeh. The combination of focal length and aperture settings can dramatically change how depth of field appears. For instance, using a wide aperture with a long focal length will produce attractive bokeh, effectively isolating the subject.
Aberrations and Distortion in Relation to Focal Length
Focal length can also lead to optical issues like aberrations and distortion.
Aberrations include optical flaws that affect image sharpness and clarity. These effects can be more pronounced with certain focal lengths, especially in prime lenses that are designed for specific uses.
With shorter focal lengths, such as those in wide-angle lenses, distortion can occur. This may appear as exaggerated perspectives, particularly at the edges of images.
In contrast, long focal lengths tend to compress objects, reducing distortion but potentially increasing issues with chromatic aberration.
Photographers can assess these characteristics through reviews to select the right lens for their needs. Understanding these nuances helps in choosing the appropriate optical systems for different photographic requirements.
