Focal length is a key concept in photography that refers to the distance from the lens to the image sensor when the subject is in focus. A common example of focal length is a 50mm lens, which is widely used for portrait photography.
This specific measurement can affect how a photo looks, influencing factors such as composition and perspective.
Different lenses with varying focal lengths create different effects in images. A wider lens, like a 24mm, captures more of the scene and is ideal for landscapes. In contrast, a longer lens, such as an 85mm, can focus closely on subjects, making it perfect for capturing details in portraits.
Understanding these differences helps photographers choose the right lens for their specific needs.
When selecting a camera lens, knowing how focal length works is essential for achieving the desired impact in photography. This understanding allows for better composition, ensuring that the images taken truly reflect the vision behind the camera.
Whether a beginner or an experienced photographer, grasping the concept of focal length can significantly enhance one’s skills and creativity in the art of photography.
Understanding Focal Length in Photography

Focal length is an essential concept in photography that affects how images are captured. It influences the field of view, depth of field, and perspective in photographs.
Different types of lenses vary in focal length, which impacts their applications in photography.
Focal Length Explained
Focal length, measured in millimeters (mm), describes the distance from the lens to the image sensor. It indicates how much of a scene will fit in the frame.
A shorter focal length, like 24mm, provides a wide-angle view, capturing more of the scene. A longer focal length, such as 200mm, results in a narrower field of view, allowing for more zoomed-in shots.
This measurement directly influences depth of field. Wider focal lengths create a greater depth of field, keeping more of the scene in focus. In contrast, longer focal lengths produce a shallower depth of field, blurring the background and isolating the subject.
Understanding this aspect helps photographers choose the right lens for their needs.
Types of Lenses by Focal Length
Lenses can be classified based on their focal lengths into several categories:
- Wide-Angle Lenses (e.g., 24mm, 35mm): Ideal for landscapes and group photos, they capture more of the scene.
- Standard Lenses (e.g., 50mm): These mimic the perspective of the human eye, suitable for everyday photography.
- Telephoto Lenses (e.g., 70mm, 200mm): Great for portraits and wildlife, they provide a narrow angle of view and excellent subject isolation.
- Macro Lenses: Designed for close-up photography, they allow for extreme detail of small subjects.
- Zoom Lenses: These cover a range of focal lengths, providing flexibility for the photographer.
Each lens type has specific uses that enhance different aspects of photography.
Focal Length and Sensor Size
Sensor size, such as full-frame and APS-C, affects how focal length translates into actual field of view.
Crop sensors have a crop factor, usually around 1.5x. This means a 50mm lens on an APS-C sensor behaves like a 75mm lens on a full-frame camera.
It’s important to consider this when selecting a lens, as the effective focal length can significantly change how images appear.
A lens’s angle of view varies depending on both its focal length and the size of the camera sensor. This relationship is crucial for achieving the desired composition in photography.
Understanding focal length and its impact on camera performance helps photographers make informed choices in their equipment and techniques.
Practical Applications and Considerations
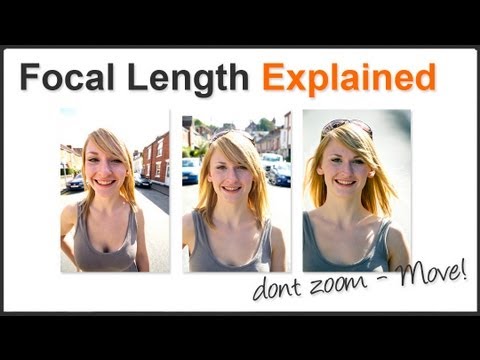
Focal length plays a crucial role in photography, influencing how images are captured across various genres. Understanding its applications can help photographers enhance their work effectively.
Focal Length in Different Photography Genres
Focal length impacts photography differently depending on the genre. For landscape photography, wide-angle lenses (under 35mm) allow for expansive views and can create a sense of depth. This helps capture entire scenes, showcasing foreground and background elements clearly.
In contrast, portrait photography often benefits from longer focal lengths, such as 85mm to 135mm. These telephoto lenses create flattering images by minimizing distortion and providing a shallow depth of field, which blurs the background. This effect focuses attention on the subject.
Wildlife photography and sports photography also favor longer focal lengths for capturing distant subjects without disturbing them. Telephoto lenses compress the scene, making it easier to photograph fast-moving subjects.
Real estate photography often uses standard and wide-angle lenses to present spaces accurately without wide-angle distortion, ensuring rooms look inviting and spacious.
Addressing Common Focal Length Misconceptions
Many misinterpret the effects of focal length.
One common belief is that zoom lenses automatically create better images than prime lenses. While zoom lenses offer versatility with variable focal lengths, prime lenses are known for their sharpness and wide apertures, which allow for beautiful bokeh effects.
Another misconception involves depth of field.
A longer focal length typically produces a shallower depth of field, isolating subjects in portraits. In contrast, wide-angle lenses have deeper depth of field, making them ideal for groups or landscapes where detail is important.
Understanding these concepts can enhance a photographer’s skill set, helping in making informed lens choices.
Photographers should consider the specific needs of their projects, whether they are using fixed focal lengths or variable focal lengths, to achieve the desired results.
For more insights, check out articles on focal length variations.

